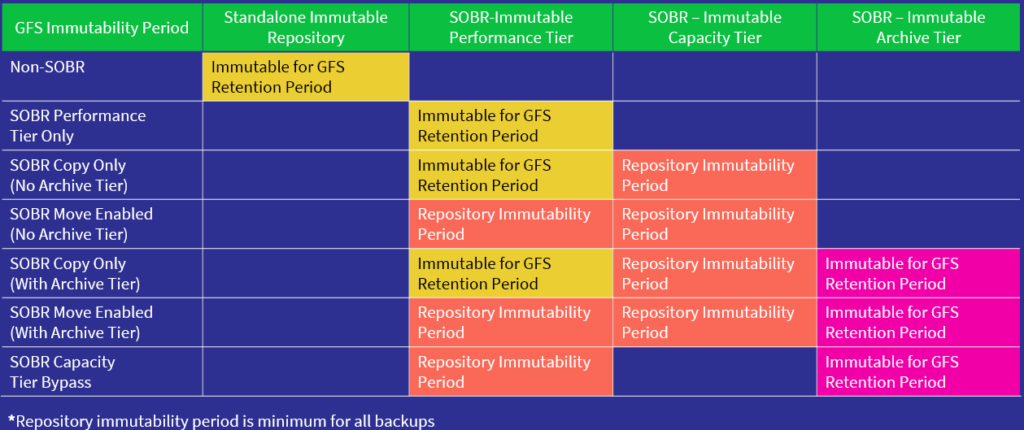
Determining immutability periods when working with Grandfather, Father, Son (GFS) backups can be a bit tricky considering GFS immutability periods can be determined by either
a) the GFS retention period
b) the Backup Repositories immutability period.
Fortunately, Fabian (@Mildur) from the Veeam R&D forums shared valuable insights that simplify this process. The full discussion can be found here.
The key takeaways from the forum discussion are as follows:
- Standalone Repositories: In the case of standalone repositories, data remains immutable throughout the GFS retention period. This means the backup data is secure and unchangeable throughout the entire GFS retention timeline.
- Performance Tier without Capacity Tier: When using the Performance Tier without the Capacity Tier, data immutability holds for the complete GFS retention period.
- Performance Tier with Move Policy Disabled: Similar to the previous scenario, if the ‘Move Policy’ is disabled within the capacity tier, the data will be immutable for the entire GFS retention period.
- Performance Tier with Move Policy Enabled: When the Move Policy is enabled within the Capacity Tier, unlike the previous example, immutability is applied as per the repository’s immutable retention period.
- On Capacity Tier: For backup data stored on capacity tier, the immutability aligns with the repository’s settings.
- On Archive Tier: Within the Archive Tier, data immutability is for the entire GFS retention period.
An essential note from the forum post highlights that if the GFS retention period is shorter than the Repository immutability period, the Repository immutability period becomes the minimum for all backup files. In other words, whichever is longer out of the two will be the immutability period.
To simplify this further, check out this fabulous table created by a fellow Veeam colleague, John Suh.